Introduction
Data breaches, intellectual property theft, identity threats, DOS (Denial-of-Service) and DDOS (Distributed-Denial-of-Service) attacks, credit card breaches, and ransomware attacks have become common methods of exploitation and theft in cyberspace.
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) controls are a set of best practices aligned with the defense in depth (DiD) strategy, which helps organizations against different threat vectors and common attacks against networks and systems. CIS controls map different security frameworks such as NIST Cybersecurity Framework, HIPPA, and PCI DSS.
CIS Controls Categories
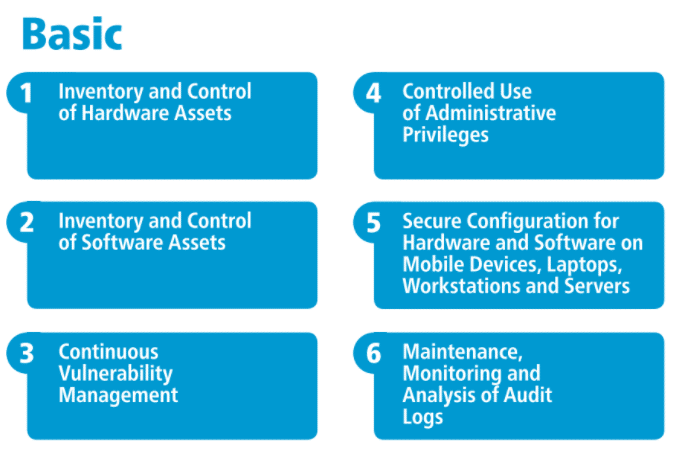
CIS’s top 20 controls are classified into three categories:
- Basic Controls
- Foundational Controls
- Organizational Controls
Basic Controls
CIS Control 1: Inventory and Control of Hardware Assets
Organizations should manage all hardware devices on the network so that only authorized devices are given privilege. By properly making an inventory and tracking the hardware, un-managed and unauthorized devices can be prevented from gaining access to the network.
Criticality of the control
Adversaries are always scanning the target organization’s perimeter, looking for loopholes and vulnerabilities that can be exploited. A single system that is not well protected and lacks system updates or patches is likely to be compromised. Attackers then compromise this system and pivot across the whole network, compromising systems and ultimately the entire network. Devices used for testing and demonstration purposes should be adequately isolated to prevent malicious attacks on the web. While executing system backups, incident responses, and recovery, the management of assets and inventory plays a vital role.
CIS Control 2: Inventory and Control of Software Assets
Organizations should manage all software on the network so that only authorized software is installed and executed. By properly inventorying and tracking all software, one can prevent the installation and execution of un-managed and unauthorized softwares.
Criticality of the control
Adversaries are always on the lookout for vulnerable software versions that they can exploit. Attackers distribute malicious software, webpages, media files via different means such as phishing, clickjacking, and social engineering techniques. The victim is compromised when they click the malicious link or install unverified software, giving the adversary remote access to their machine. Once a vulnerable software is compromised, the attacker then uses that machine to get initial access to the system or network, propagating the virus or malware throughout the organization.
While executing system backups, incident responses, and recovery, software inventory management plays a vital role.
CIS Control 3: Continuous Vulnerability Management
New information acquired should be assessed to identify new vulnerabilities, and techniques should be in place to mitigate adversaries’ risks by limiting their window of opportunity.
Criticality of the control
Security professionals are in a constant race with threat actors. Threat actors proactively try to exploit vulnerabilities while security professionals are constantly in the process of identifying vulnerabilities and deploying countermeasures.
Organizations that do not identify vulnerabilities and proactively take steps to mitigate risks increase their chances of being exploited by threat actors. Cyber defenders are constantly challenged to put the proper defenses in an organization.
CIS Control 4: Controlled Use of Administrative Privileges
The configuration of administrative privileges on systems, networks, and applications should be tracked through tools and processes to control and prevent admin access exploitation.
Criticality of the control
Exploiting administrative privileges is a widespread way used by adversaries to attack and pivot inside an enterprise. An adversary tricks a user inside an organization into clicking or downloading a malicious link or file via phishing or social engineering. The attacker, thus, gets initial access to the system and uses techniques to elevate his privileges to target an administrator account. The adversary is now able to make a malicious change in the entire network, compromising multiple systems.
CIS Control 5: Secure Configuration for Hardware and Software on Mobile Devices, Laptops, Workstations, and Servers
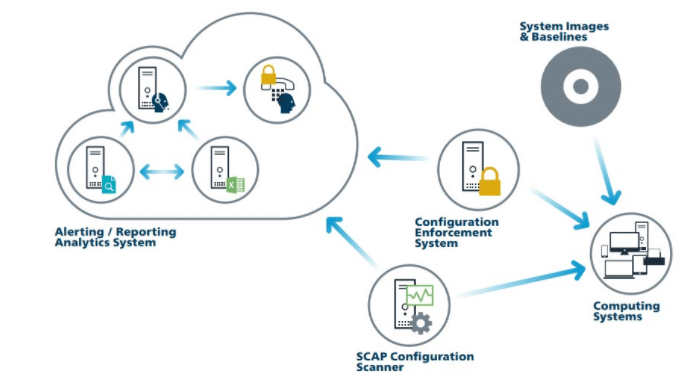
Implementing and managing security configurations on mobile devices, laptops, workstations, and servers using different security hardening techniques prevents attackers from exploiting vulnerable services and settings.
Criticality of the control
Default configurations on various devices are focused on ease of access, deployment, and use. Default configurations make it easier for attackers to quickly access a device and make malicious changes to it without any difficulty. An average user cannot make changes to the default configuration and make the device secure. Secure configuration is a continuous process that needs to be monitored and tracked to lower the chances of adversaries exploiting the device in its default state.
CIS Control 6: Maintenance, Monitoring, and Analysis of Audit Logs
Collecting, managing, and analyzing the audit logs helps detect, understand and recover from threats or attacks imposed by attackers.
Criticality of the control
The inability to analyze logs efficiently enables adversaries to control a system or network without being detected. Backdoors, viruses, rootkits, and malware remain active and hidden on a victim system for long periods in organizations that only keep logs for compliance purposes and seldom use them for detecting adversarial movements.
Foundational Controls
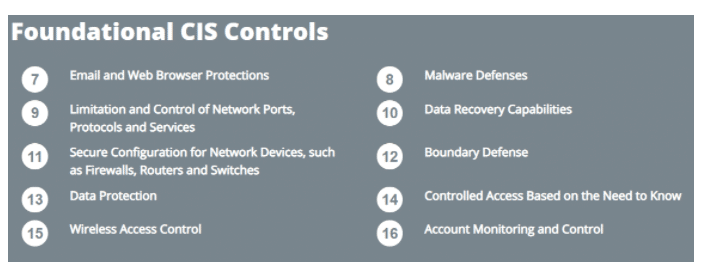
CIS Control 7: Email and Web Browser Protections
One can minimize attackers’ opportunities to exploit human behavior while interacting with email systems and web browsers.
Criticality of the control
Email clients and web browsers serve as a prevalent point of attack due to their architecture complexity, direct interaction with users, systems, and other websites. An everyday user could be enticed to access content that introduces malware. This can compromise valuable data or may lead to overall compromising of the system or application.
CIS Control 8: Malware Defenses
Controlling and limiting malware execution at different points in the organization by optimizing automation enables one to update their defense quickly, collect relevant data and take corrective action.
Criticality of the control
Malicious softwares infect and compromise systems, networks, and applications. They constantly evolve and become more sophisticated; modern malware can evade and disable defense mechanisms applied to a network or its systems.
Cyber defenders must employ such malware defenses that use automation to detect and respond to such threats rapidly.
CIS Control 9: Limitation and Control of Network Ports, Protocols and Services
Management of operational ports, protocols, and services on network devices minimizes the window of opportunity for attackers to exploit them.
Criticality of the control
Attackers search for remote network services that can easily be exploited. If web servers, mail servers, file shares, print services, and DNS servers are poorly configured, it becomes easier for attackers to use services running on them. Attackers exploit open/unused ports, file shares, and services running against these ports.
CIS Control 10: Data Recovery Capabilities
The control includes the tools and techniques to back up critical data and recover it quickly and correctly.
Criticality of the control
When attackers compromise networks or systems, they make significant changes in the configurations or softwares. An organization’s operational effectiveness is significantly decreased due to unnecessary changes and additional configurations. Once the breach is detected, appropriate techniques must be enforced to recover data and resume normal operations.
CIS Control 11: Secure Configuration for Network Devices, such as Firewalls, Routers, and Switches
Establishing, implementing, and managing network infrastructure devices’ security configuration using various hardening techniques in the change management and control process prevents attackers from exploiting services and settings.
Criticality of the control
Default configurations on various devices are focused on ease of access, deployment, and use. Use of open ports to run services, default usernames and passwords, support for older versions of softwares and protocols, etc., make a network an easy target for adversaries. Management of secure configuration is a continuous process that needs active monitoring of traffic flow and constant re-evaluation of the configuration. Attackers target poorly configured firewall rule sets, routers, and switches. They use these loopholes to penetrate a network or system’s defenses to exploit vulnerable network devices actively.
CIS Control 12: Boundary Defense
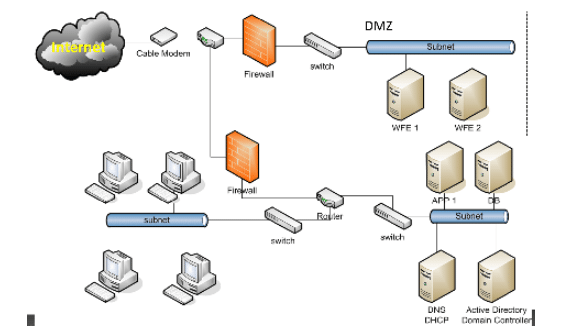
This control refers to the detection, prevention, and correction of traffic/information transferred across different trust zones of the network.
Criticality of the control
Adversaries are always on the lookout for opportunities to exploit systems that are accessible over the internet. This includes systems not only in the DMZ but also in workstations that exchange data on the internet via network boundaries. Organized crime groups and nation-state threat actors use architectural and configuration weaknesses to gain initial access into the organization. Adversaries then pivot across the network to inflict more damage to the organization.
Effective multilayer defenses in the network help defend the organization boundaries from adversary attacks.
CIS Control 13: Data Protection
Tools and processes need to be used to prevent data exfiltration. Ensure privacy and integrity of sensitive data.
Criticality of the control
Data is stored on various mediums and parts of the organization’s infrastructure. Data can be protected using different techniques such as encryption, integrity protection, and data loss prevention. Categorizing sensitive information, publicly accessible data, and less sensitive data is crucial for organizations to implement appropriate controls effectively.
CIS Control 14: Controlled Access Based on the Need to Know
Proper access control tools and processes are used to track, control, prevent and secure access to critical assets, strictly classifying users who are permitted to access and use critical and sensitive assets or data.
Criticality of the control
Encrypting data assures that if data is compromised, it is more difficult for an adversary to reveal the data unless a corresponding key to the decryption algorithm is used. The loss of control over sensitive data is a severe threat to an organization’s reputation and business operations. Adopting different encryption techniques for data on rest or in transit, data leak prevention, and access control helps prevent exposure of sensitive data to adversaries or the public.
CIS Control 15: Wireless Access Control
Appropriate tools and processes are used to track, control, and prevent risks and threats associated with using WLAN networks, access points, and wireless user systems.
Criticality of the control
Significant sensitive data and information have been exposed by adversaries who gained access to the organization’s wireless networks. Attackers find it convenient to access organizations’ wireless networks from outside by exploiting various public services. Attackers often plant backdoors by accessing wireless networks and maintaining their access to the organization’s inside network for long durations.
CIS Control 16: Account Monitoring and Control
Actively monitor and manage the life cycle of application and system accounts, their time of creation, use, deletion, and idle time, to minimize attackers’ opportunities to exploit them.
Criticality of the control
Adversaries find and target user accounts that have been dormant for a long time and use these accounts to carry out malicious activities. Malicious insiders can gain access to accounts that are left unused for an extended period.
Organizational Controls

CIS Control 17: Implement a Security Awareness and Training Program
Organizations have to identify the specific knowledge, skills, and abilities needed to deploy defenses in the organization, identify gaps, and apply remediation steps and awareness programs to keep in mind the organizational goals and objectives.
Criticality of the control
People are the weakest link in cybersecurity, and adversaries are very well aware of this. Organizations that do not educate their employees regarding new cybersecurity threats are actively exploited by adversaries using social engineering and phishing. Educating people with good cyber defense practices can lower the chance of getting exploited using human behavior.
CIS Control 18: Application Software Security
This control is about managing the security life cycle of all the softwares and applications used for the detection and prevention of security weaknesses.
Criticality of the control
Web-based applications and software programs are prone to attacks. Vulnerabilities come about in softwares due to coding errors, logical errors, etc. These vulnerabilities lead to sensitive data exposure, manipulation of configuration changes, etc.
CIS Control 19: Incident Response and Management
Organizations need to develop robust incident response and management plans for quickly discovering, containing, and neutralizing attacks.
Criticality of the control
Cybersecurity incidents have become very frequent, and almost all organizations struggle to keep up with the ever-evolving sophistication of cybersecurity attacks. Organizations must devise an incident response and management mechanism so that such cybersecurity incidents could be identified, contained, neutralized, and monitored.
CIS Control 20: Penetration Tests and Red Team Exercises
Organizations should test their network and system defense by conducting steps of penetration testing and vulnerability assessment.
Criticality of the control
Adversaries always try to exploit security loopholes in an organization. In complex business environments where technologies and cyber threats are constantly evolving, organizations should test their defenses to identify security gaps and implement appropriate mitigation steps.