Since its first recorded use in the 13th century, the word ‘hack’ has come to mean many things to many people. The words ‘hacking’ and ‘hacker’ have become polarizing terms. While some netizens find it a cool term for people who are great at breaking the rules using computers, others find it a threat.
Over time, hackers have come to take on two distinct personas: white hat hackers and black hat hackers. White hat hackers are popularly acknowledged as ethical hackers who discover weaknesses in computers and digital infrastructure and make recommendations to rectify the discovered flaws.
Black hat hackers are what people associate the term ‘hacker’ with more often. They exploit weaknesses in computers and other digital infrastructure to advance their malignant ideologies. Their actions hurt both individuals and businesses all over the world.
It’s not all doom and gloom in cybersecurity, however. It has been publicly declared that roughly 90% of all cyberattacks are caused by human error rather than technical error. This means that with increased awareness of hacking techniques, you can beat most hack attacks.
A wide variety of hacking techniques can be divided into categories and types based on the nature of the cybersecurity threats. Some of these are:
1. Brute Force Attack
This is a very common type of attack that obsolete software solutions are quite prone to. In such attacks, a hacker tries to infiltrate a user’s account by trying every possible password combination possible to guess the user’s password.
Software engineers have reduced the chances of this happening by ensuring users use really long passwords that would take a lot of time to brute force through. The password length requirement alone discourages the use of brute force attacks.
Other methods involve enforcing the use of CAPTCHA, which more or less prevents a robot from being able to carry out brute force attacks. Finally, user lockout configuration has proven to be the most effective in curbing brute force attacks by reducing the number of password tries.
2. Cookie Theft
When people access the web, they mostly aren’t aware that their browsers store and log activities other than the browser history. It may come as a surprise to many that their browser stores their password and username at times.
Hackers can gain access to this locally stored data (known as cookies) and hack a user’s account if the user accessed an unsecured website. Secure websites have a padlock image next to the URL address, which is an indicator. Software engineers are usually encouraged to secure websites.
3. Denial Of Service
If you’ve ever bitten more than you can chew, then you probably understand what denial of service feels like. It’s a situation where hackers mobilize a lot of compromised computers and use those computers to jointly assault a system and overwhelm it with traffic to destabilize the system.
There are several ways of handling denial of service. Any organization can guard against denial of service with proper planning involving the participation of DevOps engineers and cybersecurity experts. A common way organizations do this is by making use of the cloud infrastructure to shore up the strength of their digital infrastructure.
4. Phishing Attacks
If you’re wondering whether there’s a reason why this sounds a lot like fishing, then you’re right—it’s not a coincidence. With Americans losing roughly $50 million to phishing scams in 2019 alone, you need to be cautious about such attacks.
This attack works by baiting unsuspecting victims into clicking links that are perceived as legitimate and tricking victims into handing over sensitive data or credit card information that is then used to defraud them.
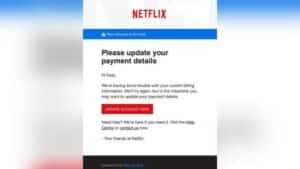
These phishing attacks usually come as emails disguised as some “too good to be true” reward, requests to update your details online, information that you should register for some financial reward and whatnot. If it sounds too good to be true it usually is.
By being very careful of emails and sudden requests for your private or financial information by unverified entities one can guard against phishing attacks.
5. SQL Injection
SQL stands for structured query language. An SQL injection occurs when a user inputs SQL queries in an input field to gain illegitimate access to a database. SQL is a language that can be used to manipulate a database. A database is where all data about users or information used by a digital infrastructure is stored.
SQL Injections can be thwarted using parameter queries, stored procedures, input validation, among other methods. By far, the easiest to set up is input validation on the client-side and server-side through the use of regular expressions and declarations that limit the number of characters that a user can fill in an input box.
Proper Risk Evaluation
Proper risk evaluation involves assessing yourself as a person and a professional to know how much of a high-value target you are. The average person may not attract more than basic hacking techniques like phishing. However, high-value targets need to invest in more robust cybersecurity measures.
If you’ve heard of or watched Shark Tank you may have heard of Barbara Corcoran, a Shark Tank host who was scammed of roughly $400,000 by a simple phishing attack. The attacker used an email address that looked similar to the one belonging to Barbara’s assistant.
Depending on their size, organizations need to invest in either cybersecurity consultants or a cybersecurity department within the organization to guide against both pranksters and malignant hackers. While the cost of hiring a cybersecurity team seems like a lot, one has to look at it like insurance.
Public sector organizations need to invest a lot more than the average company, as these organizations are subject to cybercrime, politically motivated cyberattacks, and cyberterrorism. Ultimately, the entity involved determines the cybersecurity measures that must be enacted.
Final Thoughts
There are so many hacking techniques that netizens, corporate organizations, and governments need to worry about. With hackers getting smarter every day, it may seem too daunting a task to protect your computers and digital resources from hackers continuously. But, by being careful of the kind of websites, links, and digital resources you access, you can protect yourself from most attacks. Most importantly, evaluating yourself and your organization can help you prevent and guard against hacking attacks.