Defense in-depth (DiD) is a layered cybersecurity approach/strategy in which multiple defenses are placed across the IT infrastructure to protect it from various malicious attack vectors. The DiD strategy creates multiple layers of network/system defenses, if one security defense fails the other takes over. This approach helps organizations tackle various sophisticated attack vectors very effectively and efficiently.
To better understand the concept, an analogy of a castle can be considered. In the Medieval ages, castles were protected from enemy attacks by building thick walls around them. For an enemy to penetrate the castle they had to face several defenses such as moats, draw bridges, towers with archers etc. These obstacles slowed down the attacking stance of the enemies and bought time for the king to consider his response and deploy countermeasures. Similarly, the DiD strategy employs different network security measures and techniques that work in layers, slowing the attacker and decreasing the impact of the attack.
Importance of DiD
Cybersecurity threats and attacks have evolved and become more sophisticated. A single network defense mechanism is not enough to counter attacks and threats. A poor network defense will eventually leave the network and systems very vulnerable to malware attacks, phishing attacks and ransomware, leading to damages worth millions and compromising the confidentiality, integrity and availability of customer data.
According to IBM, the global average total cost of data breaches recorded in 2020 was approximately $3.86 million.

Source: IBM
The data breaches will continue to remain persistent and destructive in the future. So, the need for strong defenses is very essential for different businesses, enterprises and campus networks. The DiD approach reduces the probability of a single point of failure.
According to NIST Special Publication 800-27 Rev A Section 3.3.4 Principle 16:
Implement layered security (ensure no single point of vulnerability). Security designs should consider a layered approach to address or protect against a specific threat or to reduce a vulnerability. For example, the use of a packet-filtering router in conjunction with an application gateway and an intrusion detection system increase the work-factor an attacker must expend to successfully attack the system. Adding good password controls and adequate user training improves the system’s security posture even more.
The need for layered protection is especially important when commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) products are used. Practical experience has shown that the current state of security quality in COTS products does not provide a high degree of protection against sophisticated attacks. It is possible to help mitigate this situation by placing several controls in series, requiring additional work by attackers to accomplish their goals.
DiD Architecture
The DiD architecture comprises the following key layers:
- Administrative Controls
- Technical Controls
- Physical Controls
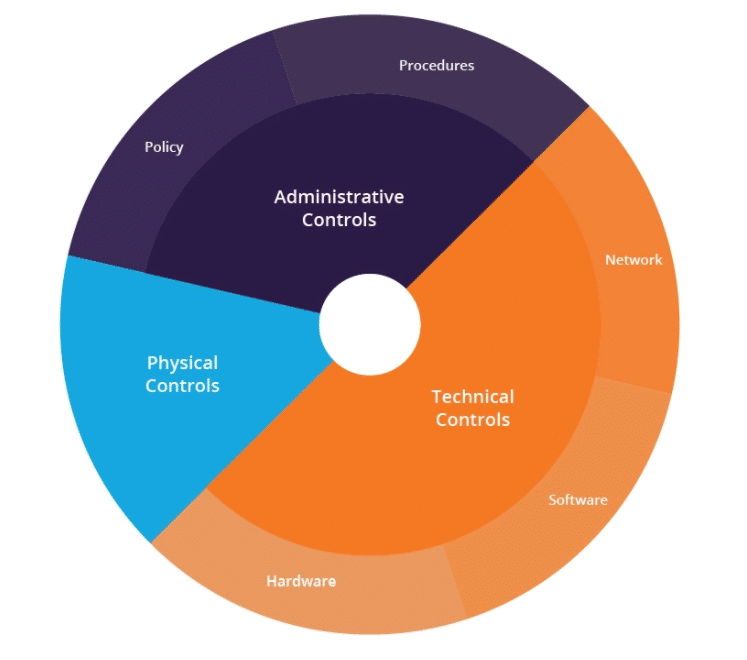
Source: Imperva
To implement the DiD strategy in our enterprise or corporate network, it is necessary to get to know each of the key components as mentioned earlier
- Administrative Controls:
Administrative controls comprise the policies and procedures of the organization. The purpose of administrative controls is to ensure that proper guidance is available when dealing with administrative changes and making sure that regulations are met. The hiring process, security standards implementation, scrutiny of employees are some of the administrative controls.
- Technical Controls:
These are the controls that include the security measures and controls that are implemented to secure the network from different types of malicious attack vectors. These controls are deployed and implemented in the IT infrastructure and can in the form of software or hardware
Some of the technical controls are mentioned but not limited to the following :
- Next-Generation Firewalls
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
- Antivirus & Malware Detection
- Virtual Private Networks
- Encryption aAnd Hashing
- Biometric Verification
- Proxy Servers
- Password Management
- Physical Controls
Physical controls consist of security solutions that protect the physical systems present in the IT infrastructure.
Below are some essentials physical controls
- Locks
- CCTV Cameras
- Motion Sensors
- Security Guards
- Metal Detectors
- Keycards
Network Security Policies and Techniques
Network security policies guide implementing secure network security controls on an organization’s IT infrastructure. It mentions a set of rules that are under the information security goals and objectives. A network security policy should include all the security requirements that an organization is willing to implement on its network and systems.
These are policies and techniques that an organization implements to secure its IT infrastructure and important assets
- Access Control
- Firewall Rules and policies
- User Access Management
- Remote Connection Policies
- Intrusion Detection & Prevention Rules
- Implementation of Virtual Private Network
- Segregation of Network into zones i.e. Trust, Untrust, Internet, Local & DMZ(Demilitarized Zone)
- Logs and Packet Analysis
- Endpoint Protection
- WLAN Security Policies
- Data Loss Prevention Techniques
- Web Security / WAF
- Application Security
Conclusion
Implementing DiD ensures network security and an organization’s preparation towards handling complex malicious attacks. The DiD strategy slows down the adversarial attacks and buys more time for organizations to respond with the appropriate countermeasures before the impact of the threat propagates itself throughout the network. Implementing the DiD strategy is resource-intensive and takes time but it eventually enables organizations to protect their critical systems and networks from sophisticated attacks.